Have you ever wondered how some people manage to preserve their eyesight and eye health well into old age? The secret might lie in a nutrient known as lutein. In this blog post, you’ll discover what lutein is, its crucial role in maintaining good eyesight, and how you can start including it in your diet today.
What Lutein is?
Lutein is a type of carotenoid, which is a group of antioxidants found in many plant species. These pigments give fruits and vegetables their vibrant red, orange, and yellow colors. By improving plant health, foods rich in lutein offer numerous health benefits to people.

Benefits of Lutein for Eye Health
1.Suppresses Inflammation
Lutein has strong anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce eye inflammation and may prevent various eye conditions.
2.Defends Against Free Radicals
As an antioxidant, lutein helps neutralize free radicals, which reduces oxidative stress and protects eye cells from damage.
3.Enhances Visual Performance
Lutein enhances visual performance by improving contrast sensitivity and reducing glare, leading to sharper vision.
4.Protects Eye Tissue
Lutein absorbs harmful blue light, protecting eye tissues from sunlight damage and lowering the risk of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
5.Supports Retinal Health
Lutein and zeaxanthin are concentrated in the macula region of the retina, essential for converting light signals into electrical signals and transmitting them to the brain.
Lutein and Eye Conditions
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Lutein may help protect against AMD, a leading cause of blindness in developed countries.
Diabetic Retinopathy
It might reduce oxidative stress markers in diabetic retinopathy, potentially preventing vision loss.
Cataracts
A diet low in lutein is associated with a higher risk of developing cataracts. Lutein can help maintain the clarity of the lens.
Dry Eye Disease
Lutein can alleviate symptoms of dry eye disease, such as redness, itchiness, and burning sensations.
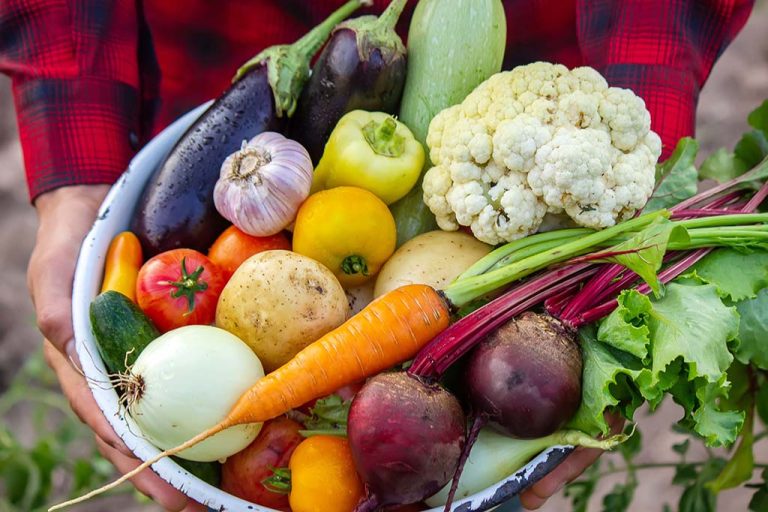

Natural Sources of Lutein
Incorporating lutein into your diet is simple with these foods:
- Kale and Spinach: Rich sources of lutein.
- Broccoli and Lettuce: Packed with lutein and other essential nutrients.
- Parsley and Basil: Herbs that add flavor and nutrients.
- Leeks and Peas: Versatile and nutritious.
- Egg Yolks: A convenient source of lutein.
- Red Peppers and Corn: Bright and lutein-rich.
How Much Lutein Do You Need?
While there’s no official daily recommended intake for lutein, research suggests that consuming 6-10 mg per day can provide significant eye health benefits. Many people consume only 1-2 mg daily, so focusing on lutein-rich foods or considering supplements is essential.
Lutein works best with other nutrients such as:
- Vitamin C: Regenerates antioxidants and supports eye tissue.
- Vitamin E: Protects retinal cells from oxidation.
- Zinc: Essential for transporting vitamin A to the retina.
- Essential Fatty Acids (DHA): Preserves vision and reduces inflammation.
Conclusion
Lutein is one of the important nutrients that are required to keep the eyes healthy and to avert vision complications. You also need to incorporate foods with lutein in your meals, and if this is still not enough, find appropriate supplements to preserve your vision and prevent eye problems. So the next time you are cooking a dish do not fail to include the green part of some vegetables, or a couple of egg yolks for a shot of lutein!
To add more details, find out on “What is Lutein”.

